

- #Sql tabs postgresql super user install
- #Sql tabs postgresql super user serial
- #Sql tabs postgresql super user update
The space for the maximum possible protected relations is reserved during database server startup.Įdb_sql_protect.max_queries_to_save. Every protected relation consumes space in shared memory. The total number of protected relations for the server is the number of protected relations times the number of protected roles. Sets the maximum number of relations to protect per role. The default is 64.Įdb_sql_protect.max_protected_relations. Sets the maximum number of roles to protect. See Setting the protection level for more information.Įdb_sql_protect.max_protected_roles. Sets the action taken by SQL/Protect when a SQL statement is issued by a protected role. The default is off.Įdb_sql_protect.level. When you're ready to begin monitoring with SQL/Protect, set this parameter to on. Controls whether SQL/Protect is actively monitoring protected roles by analyzing SQL statements issued by those roles and reacting according to the setting of edb_sql_protect.level. Add $libdir/sqlprotect to the list of libraries.Įdb_sql_protect.enabled.
#Sql tabs postgresql super user install
#Sql tabs postgresql super user serial
Testdb=> CREATE TABLE anothertable (id SERIAL NOT NULL) You can also use triggers and other approaches to set the role automatically on table creation. If we call SET ROLE cloudsqlsuperuser before creating our table, the owner will now default to the cloudsqlsuperuser role, which will allow postgres and other members of the role the default permissions assigned to the role by default: However, when doing so, they will by default have their owner set to the user which created them, rather than the parent role: testdb=> CREATE TABLE sometable (id SERIAL NOT NULL) Testdb | cloudsqlsuperuser | UTF8 | en_US.UTF8 | en_US.UTF8 |Īccordingly, members of the cloudsqlsuperuser role will have permissions to create objects in the database by default. Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges (As shown in the above role listing, the cloudsqlsuperuser role is inherited by the postgres user.) List of databases
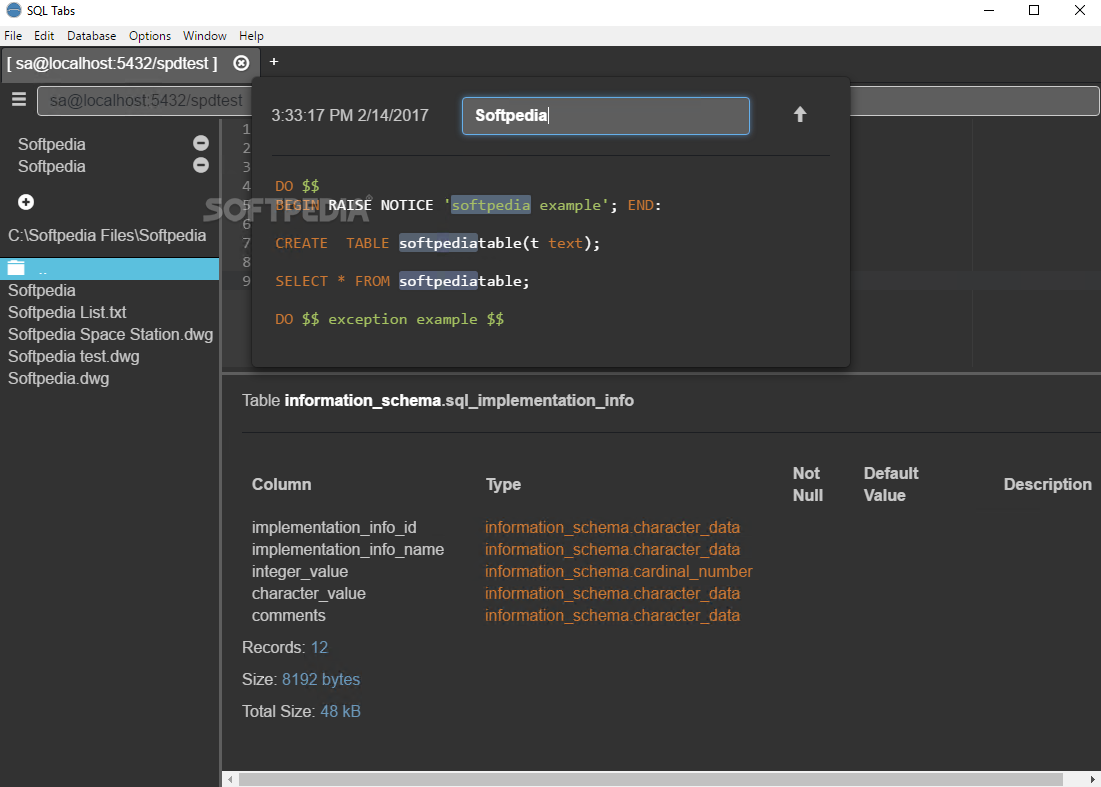
Moreover, new databases created using the "Databases" tab in the Cloud Console have ownership assigned, by default, to the cloudsqlsuperuser role.

+-+-Īcando14 | Create role, Create DB | I have this situation about users : Role name | Attributes | Member of How can I query the data in the database with the postgres user? The response is Insufficient privilege: 7 ERROR: permission denied for relation
#Sql tabs postgresql super user update
Enter my Symfony ( phpfpm) pod and run the command php bin/console doctrine:schema:update -force to update the schema.Add proxy to k8s container to connect to the Cloud SQL instance with all credentials, as described in the GCP documentation.I follow these steps to create and populate the database (without success):
My tech stack consists of hosting my application in a Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE) deployment, using the Cloud SQL proxy sidecar to connect to the database within the pods. I am struggling to solve this problem with Google Cloud Platform's Cloud SQL component.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
